Get better faster
DocTap offers same-day GP appointments and instant onsite testing - so you can get diagnosed and treated faster.

- patients treated
- 500,000
- London clinics
- 9
- of patients recommend
- 94%
- test results (Kings Cross & Liverpool St)
- 15 min
Healthcare reimagined
Everything you need to get better quickly

Locations
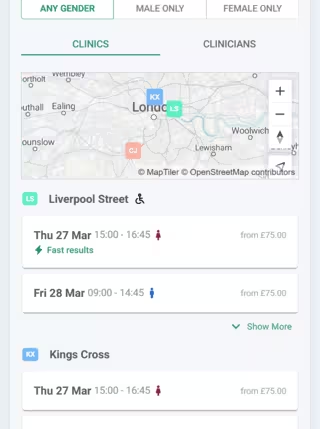
9 London clinics
Choose between clinic and video appointments depending on your needs and location.
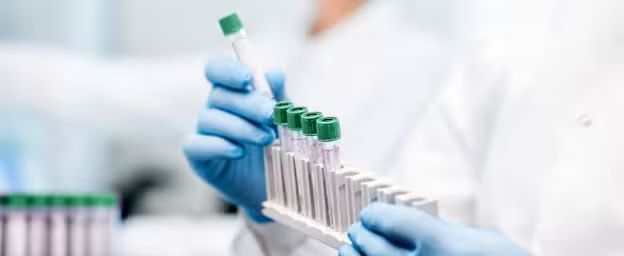
Onsite laboratory
Instant test results
With results ready in minutes, you can receive your diagnosis and treatment that day. (Liverpool St only)

Medications
In clinic dispensing
Many medications are stocked in clinic, saving you a trip to the pharmacy.

Continuity of care
Choose your clinician
Select from male and female clinicians, or filter by those you've seen before.

Real-time availability
Book online now
Same day, evening and weekend appointments available.

Very thankful to DocTap - super attentive, supportive and willing to help so I can only recommend them! My doctor was extremely caring and knowledgable and took the time to really listen to me. Booking was also very smooth - I could get an appointment for the same or next day. And there was a smiling and very helpful receptionist to help me when I arrived at the clinic. Thank you DocTap!
Ready to book?
Easily view availability and prices by location, date, and clinician. Book a same-day appointment today.
Services

GP Services
Expert medical advice and diagnosis from our caring, GMC-registered doctors.
- Prescriptions
- Tests & scans
- Letters & sick notes
- Referrals

Sexual Health
Confidential testing and treatment for both symptomatic and asymptomatic patients.
- STI tests from £60
- Same day appointments
- 4 hour results
- With or without a GP

Health Screens
Comprehensive health screens for peace of mind and early detection of health issues.
- Health screens from £50
- Same day appointments
- Same day results + report
- With or without a GP

Mental Health
Compassionate, confidential support for mental health challenges from our experienced clinicians.
- Counselling & talking therapy
- Antidepressant prescriptions
- In person and video consultations
- GP sickness letters
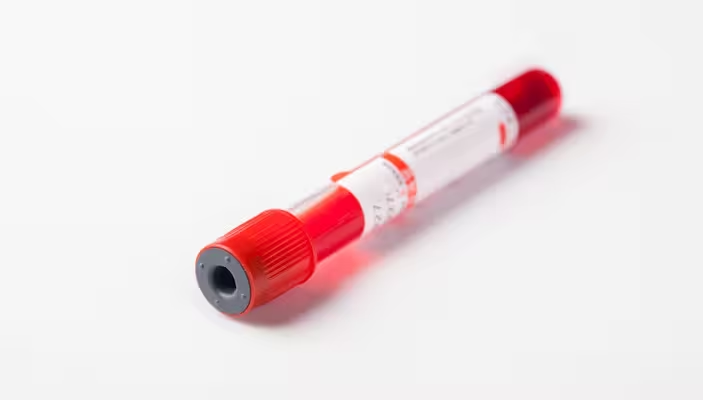
Tests & Scans
Fast, reliable blood testing with quick results, for prompt diagnosis and peace of mind.
- 1000+ tests available
- Same day results on many tests
- MRIs, ultrasounds, x-rays
- Includes GP interpretation
Find a Clinic
Choose from 9 London clinics, each conveniently located near major transport links or business hubs.
- Check availability online
- Onsite lab in Liverpool St. clinic
- Common medicines dispensed in clinic
- Video appointments also available
How it works
Get started in minutes
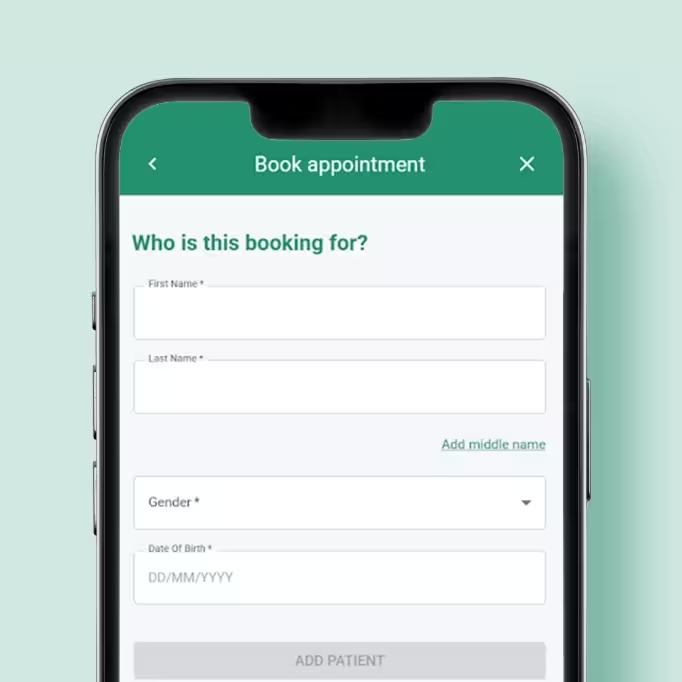
- 1Find an appointmentClick 'Book' and choose a convenient clinic or video appointment.
- 2RegisterEnter you name, gender, telephone, email and address. That's it.
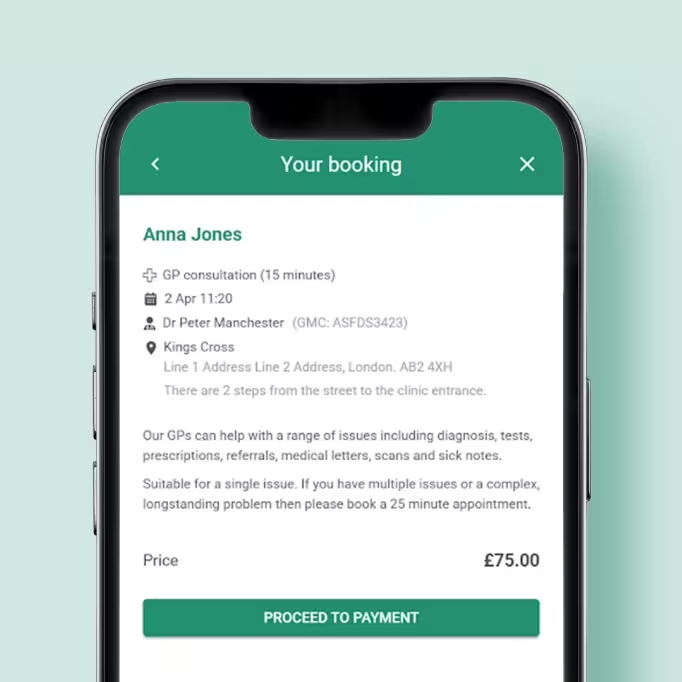
- 3Confirm your bookingPayment is taken on booking, with appointment details available in your patient portal and sent by email.
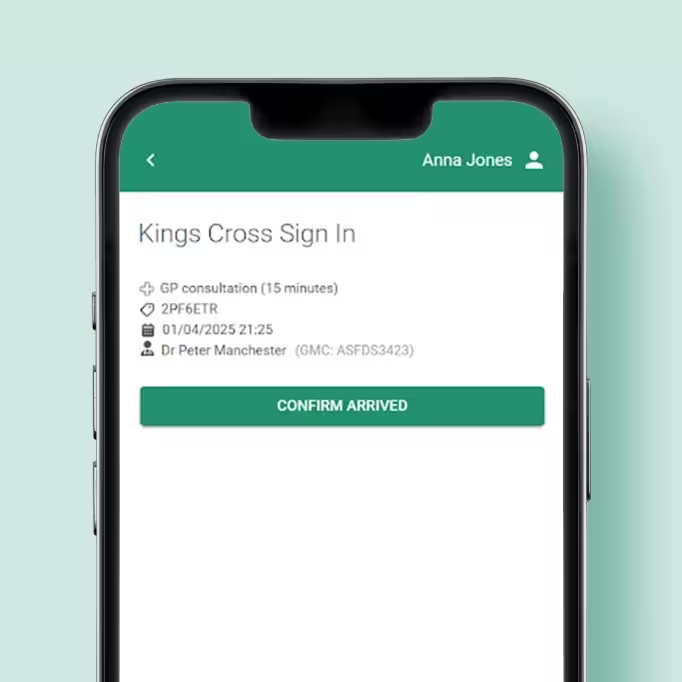
- 4Attend your consultationOur clinicians combine expert medical care with a compassionate, patient-focused approach.
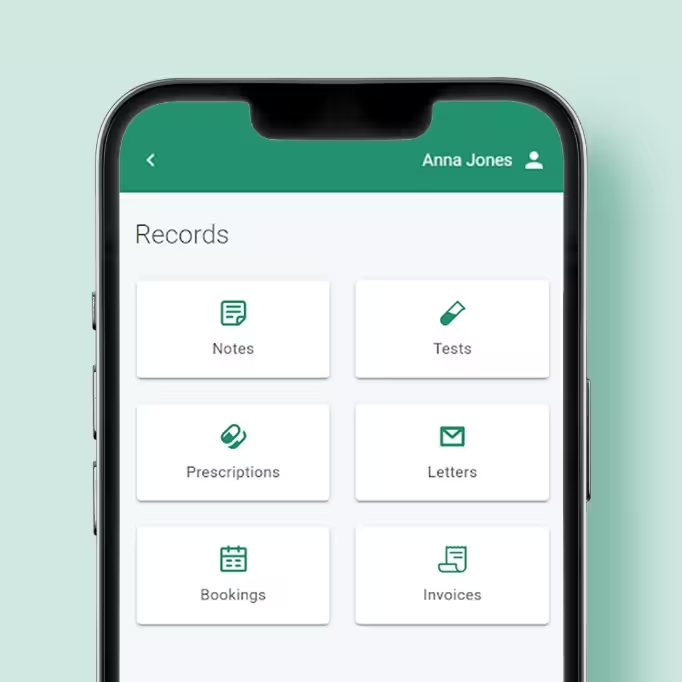
- 5AftercareAccess your medical records in the patient portal, where you can request support or schedule a follow-up.
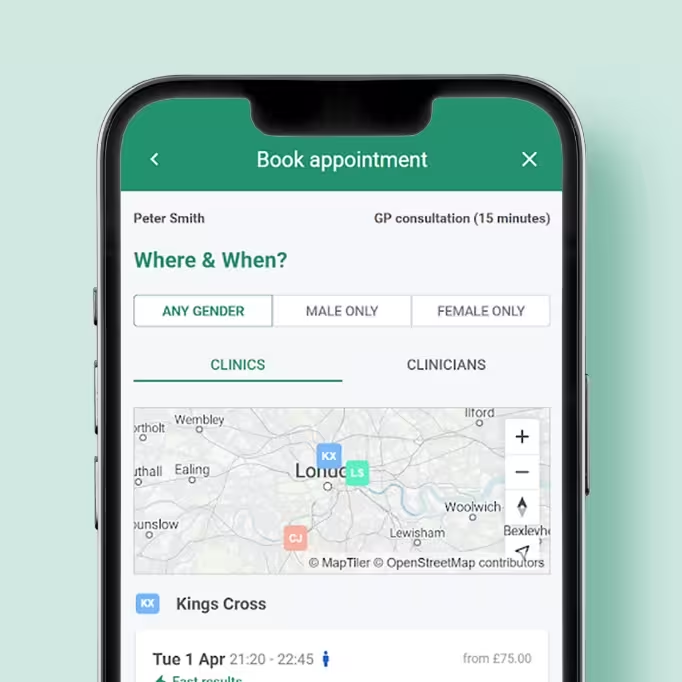
Experience the world’s easiest healthcare booking system.
DocTap Platform
You're in control
Book an appointment
Quickly view availability by location, time and clinician. Prefer a video call for this appointment - no problem.
Notifications
View updates to your records and get notified when results or letters are released.

Support
Raise and track any support requests following your appointment.

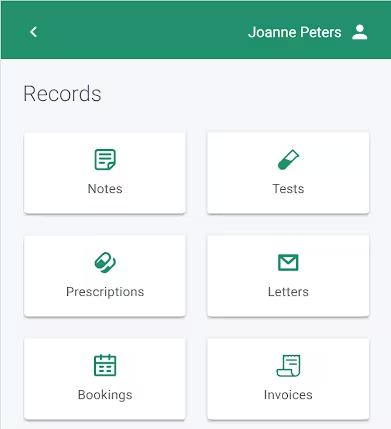
Medical records
View your medical records, prescriptions, results and letters.
We care about your care
Our values
- Evidence based medicine.
- Our clinicians are not incentivised to recommend unnecessary tests or procedures. We do not offer alternative or cosmetic medicine.
- Patient centred care.
- We treat patients with compassion, dignity, and respect, taking the time to explain things in clear English.
- Continuity of care.
- Whenever possible, test results are reviewed by the clinician who ordered them. You can also choose to see the same clinician for follow-ups.

Onsite Laboratory
Instant test results
Instant tests only available at Kings Cross & Liverpool St.
- Blood tests:
- Full blood count, liver, kidney, thyroid, cholesterol, HbA1c, testosterone and CRP.
- STI tests:
- HIV, chlamydia, gonorrhoea, syphilis, herpes, trichomonas, hepatitis B and C.
- Test and treat.
- Book a blood test for 15 minutes before your GP appointment, and your results will be ready to review in the consultation.
- Sorted same day.
- Not sure if you need any tests? Book with a GP, who will take any necessary tests in the appointment and report on the results later that day.

